Advanced Excel - Additional Features - Power View in Excel 2013 provides an interactive data exploration, visualization, and presentation experience for all skill levels as you have seen in the previ. Whether you are a Microsoft Excel beginner or an advanced user, you'll benefit from these step-by-step tutorials. Microsoft Excel was first released in 1985, and the spreadsheet program has. Updates for Get & Transform and the Power Query add-in. More enhancements when you add a column from examples: In the Query Editor, Column from Examples has been improved to support suggestions, more Date/Time operations, and additional transformations. New Azure Data Lake Store connector: We're always working to add new connectors. Now you can import data from an Azure Data Lake Store.
Whether you're just starting out on your Excel journey or have been using it for a while, there are a few skills that you should know about Excel: the best ways of doing things, certain pitfalls to avoid, things that will impress other people (especially your boss).
In this article, I will talk about the 20 most important skills you need to know about Excel, including some of the best hints and tips I can think of to get you started as a beginner – or make you more productive as an experienced user.
Table of Contents
1) Converting to PDF
You probably need to send out an Excel spreadsheet or report to clients quite often – but do you want them looking at all your data and formulas? Probably not.
Although there's a number of ways to stop people looking at and changing things on your spreadsheet (you can hide things, protect things, or disguise values with formatting), with a little bit of know-how, all these methods can be circumvented.
As with everything else, often the simplest route is the best. If you want to prevent other people from changing your data, simply convert your spreadsheet to PDF and send out that. Android connect to pc software. Converting Excel documents to a PDF file is simple and all current versions of Excel can do it without the need for additional software.
If you need some help with this (or if you're looking for similar tips and tricks), Activia Training has launched a new section on their website which has some great tutorials and how-to videos.
Read More: Excel Advanced Filter Tutorial
2) Using the Fill Function
Let's say you need to keep 12 months of complex accounts in one workbook. You have created 12 sheets and named them January to December, laid out and formatted the January sheet, and then proceed to copy and paste the spreadsheet to the other 11 sheets.
This is a tedious method and if the data is pasted incorrectly, it may even prevent you from quickly generating a summary sheet later on. In fact, the best method for doing this is to use Excel's 'Fill Across Sheets' tool. Using the Fill function will allow you to duplicate one sheet across many others quickly and accurately.
If you need some additional help with using this feature, Tom has a great step-by-step tutorial on his blog.
3) Using Named Ranges
I have a formula here that sums the total of three different ranges on three separate sheets: Fuel for keynote themes 2 0 2.
=SUM(‘Jan Sales'!$D$10:$L$10, ‘Feb Sales'!$D$10:$L$10, ‘Mar Sales'!$D$10:$L$10)
And another one that does the same thing:
=SUM(JanTotal, FebTotal, MarTotal)
Master Excel Formulas & Functions in Just 3.5 Hours!
with my FREE COURSE at Udemy.
Which one do you prefer? Personally, I like the second one, since it's much easier to understand and it was much easier to create as well – I never had to go to the other sheets to select the data ranges.
The second formula makes use of so-called named ranges. Named ranges (or defined names) apply to a single cell or a range of cells and, as you can see in the formula, can be used as a direct replacement for the cell or range address.
Named ranges are also intrinsically absolute, so no need for dollar symbols to anchor refs. Named ranges are also, by default, global – so when you create a named range on one sheet, you can use that name on any other sheet and it always refers back to its original location.
Read More: Top 20 Excel Limitations that might Frustrate You!
4) Formatting
Once you've created your spreadsheet, you're going to do either of two things: enter data or review data. Neither of these things is helped by a proliferation of fonts, sizes, and colors.
To make your spreadsheet easier to understand, try to pick one font and stick with it. Use emphasis (bold or italics) to highlight differences between headers and data, and use light cell coloring to pick out summary rows and formulas.
Finally, leave all the formatting till last. A working spreadsheet with no formatting may not look good, but it works. An unfinished spreadsheet that looks fantastic is, however, useless.
The formatted worksheet is more user-friendly [click on the image to get an enlarged view].
5) Choosing the Right Layout
It may seem obvious but a lot of people just open Excel, start typing, and hope for the best. However, you need to do a little planning before you dive in and start creating a spreadsheet. Generally, we tend to understand the data that we need to get into the spreadsheet, but give little thought about what we actually want to get out of it.
Have a good think about what you hope to get out of the spreadsheet and make sure that you layout your spreadsheet in a way that will achieve this.
6) Protecting Your Work
You have gone to a great deal of trouble designing the perfect spreadsheet, so the last thing you need is someone opening it and accidentally overwriting a formula, or changing something they are not supposed to change. And this is where protection comes in.
Read More: 15 Best Basic & Advanced Online Excel Training Courses!
Excel has some great tools for protecting your work and controlling what your users can change. You can protect formula cells to stop them from being changed, stop columns or rows from being resized or even stop the user from changing the structure of the workbook by adding or deleting sheets. At an advanced level, you can even allow only certain users to edit particular regions.
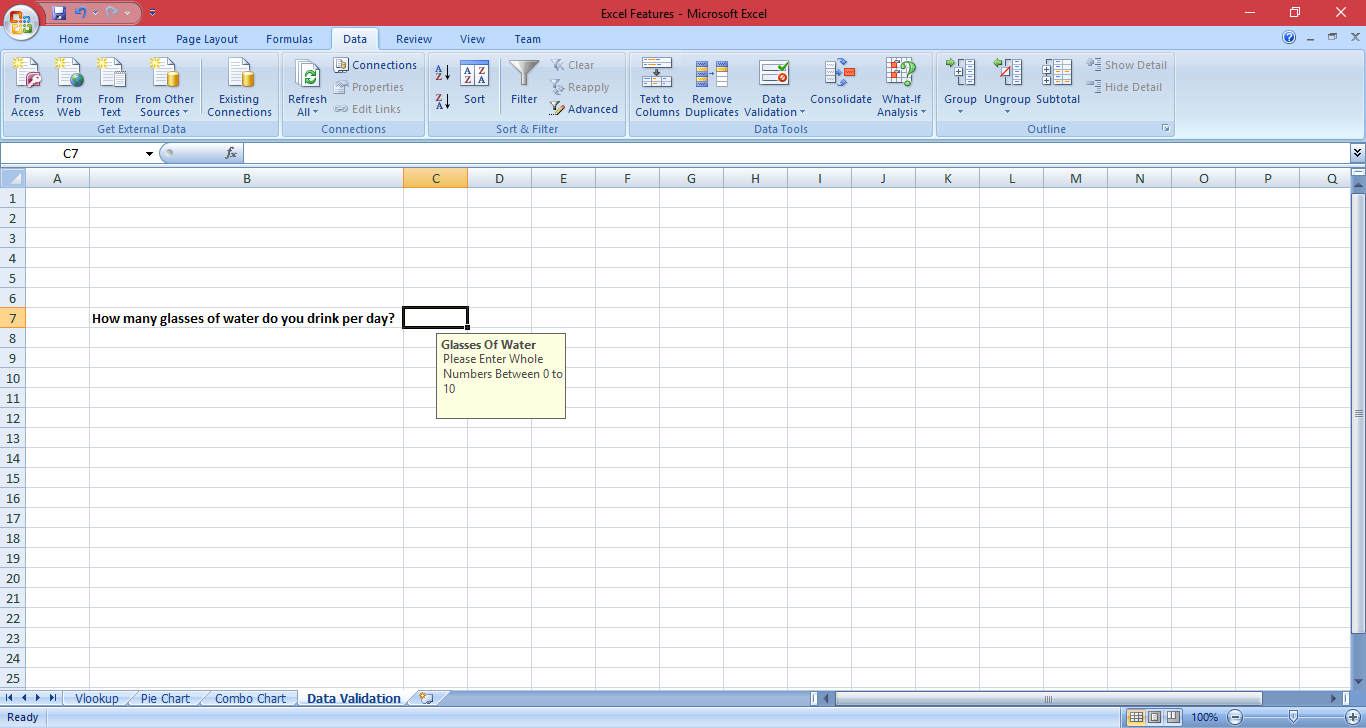
7) Controlling Data Input
For me, one of the most frustrating things to see in Excel is incorrect data. Dates are the biggest culprits since some people insist on entering dates the wrong way and what looks like a date on the sheet is actually just text. Not only does this create more work down the line, but it can also end up causing formulas to go wrong and filters not to work.
The solution? Data validation. By using data validation, not only can you control the type of information the user enters into cells (such as dates, numbers, or text) but the range of data as well.
Sometimes if you don't control the data input, your user might make the worksheet a mess.
Read More: Excel Advanced Filter Tutorial
2) Using the Fill Function
Let's say you need to keep 12 months of complex accounts in one workbook. You have created 12 sheets and named them January to December, laid out and formatted the January sheet, and then proceed to copy and paste the spreadsheet to the other 11 sheets.
This is a tedious method and if the data is pasted incorrectly, it may even prevent you from quickly generating a summary sheet later on. In fact, the best method for doing this is to use Excel's 'Fill Across Sheets' tool. Using the Fill function will allow you to duplicate one sheet across many others quickly and accurately.
If you need some additional help with using this feature, Tom has a great step-by-step tutorial on his blog.
3) Using Named Ranges
I have a formula here that sums the total of three different ranges on three separate sheets: Fuel for keynote themes 2 0 2.
=SUM(‘Jan Sales'!$D$10:$L$10, ‘Feb Sales'!$D$10:$L$10, ‘Mar Sales'!$D$10:$L$10)
And another one that does the same thing:
=SUM(JanTotal, FebTotal, MarTotal)
Master Excel Formulas & Functions in Just 3.5 Hours!
with my FREE COURSE at Udemy.
Which one do you prefer? Personally, I like the second one, since it's much easier to understand and it was much easier to create as well – I never had to go to the other sheets to select the data ranges.
The second formula makes use of so-called named ranges. Named ranges (or defined names) apply to a single cell or a range of cells and, as you can see in the formula, can be used as a direct replacement for the cell or range address.
Named ranges are also intrinsically absolute, so no need for dollar symbols to anchor refs. Named ranges are also, by default, global – so when you create a named range on one sheet, you can use that name on any other sheet and it always refers back to its original location.
Read More: Top 20 Excel Limitations that might Frustrate You!
4) Formatting
Once you've created your spreadsheet, you're going to do either of two things: enter data or review data. Neither of these things is helped by a proliferation of fonts, sizes, and colors.
To make your spreadsheet easier to understand, try to pick one font and stick with it. Use emphasis (bold or italics) to highlight differences between headers and data, and use light cell coloring to pick out summary rows and formulas.
Finally, leave all the formatting till last. A working spreadsheet with no formatting may not look good, but it works. An unfinished spreadsheet that looks fantastic is, however, useless.
The formatted worksheet is more user-friendly [click on the image to get an enlarged view].
5) Choosing the Right Layout
It may seem obvious but a lot of people just open Excel, start typing, and hope for the best. However, you need to do a little planning before you dive in and start creating a spreadsheet. Generally, we tend to understand the data that we need to get into the spreadsheet, but give little thought about what we actually want to get out of it.
Have a good think about what you hope to get out of the spreadsheet and make sure that you layout your spreadsheet in a way that will achieve this.
6) Protecting Your Work
You have gone to a great deal of trouble designing the perfect spreadsheet, so the last thing you need is someone opening it and accidentally overwriting a formula, or changing something they are not supposed to change. And this is where protection comes in.
Read More: 15 Best Basic & Advanced Online Excel Training Courses!
Excel has some great tools for protecting your work and controlling what your users can change. You can protect formula cells to stop them from being changed, stop columns or rows from being resized or even stop the user from changing the structure of the workbook by adding or deleting sheets. At an advanced level, you can even allow only certain users to edit particular regions.
7) Controlling Data Input
For me, one of the most frustrating things to see in Excel is incorrect data. Dates are the biggest culprits since some people insist on entering dates the wrong way and what looks like a date on the sheet is actually just text. Not only does this create more work down the line, but it can also end up causing formulas to go wrong and filters not to work.
The solution? Data validation. By using data validation, not only can you control the type of information the user enters into cells (such as dates, numbers, or text) but the range of data as well.
Sometimes if you don't control the data input, your user might make the worksheet a mess.
8) Using Keyboard Shortcuts
Most people just reach for the mouse when they want to perform an action in Excel, but with a few keyboard shortcuts, you can speed up your work and save a great amount of time. Here are a few to get you started:
| Keyboard Shortcut | Function |
| Ctrl + * | Select the current region |
| Ctrl + Space | Select the current column |
| Shift + Space | Select the current row |
| Ctrl + 0 | Hide the current column |
| Ctrl + 9 | Hide the current row |
| F4 | Apply absolute refs (in a formula) |
| F3 | Shows the name box (in a formula) |
| Ctrl + : | Enter the current date |
| Alt + = | Auto-sum the adjacent data |
9) Saving Time with Auto-fill
Just enter a formula and need to use the same thing in adjacent cells? Instead of typing the formula again, you can use auto-fill. Auto-fill allows you to quickly copy the values from one cell to lots of adjacent cells, either vertically or horizontally.
Read More: How to Make an Excel Add-in [Narrated with an Example]
And it doesn't just work with formulas either, you can use auto-fill to quickly create lists of days, months, or even create your own lists. Auto-fill will also automatically increment dates and numbers for you, saving you lots of time in the process.
10) Finding Key Values Quickly
With large sets of numbers, it can be difficult to find the values that are the most interesting or important: just the top 10 values, everything above average, duplicate values. Conditional formatting makes short work of highlighting key values based on simple rules. And the best thing is when the values change, conditional formatting kicks in and re-formats the cell accordingly. You can use ExcelDemy.com's epic guide on Excel conditional formatting.
11) Analyzing Large Data Sets
One of Excel's main tasks is to organize data, and with the new versions of Excel able to handle over a million rows, you can have a lot of data. And when you need to get answers to complex questions from this data, it has all the tools you need.
Pivot tables can be scary beasts to the uninitiated, but once you understand how they work, you will quickly see how easy they can be and how useful they are at summarizing and organizing data. And all this with just a few clicks!
Read More: Excel Dynamic Named Range [4 Ways]
12) Customizing the Ribbon
I love the ribbon, but it can be a bit irritating having to switch from one tab to the other to find the commands you want to use. The good news is that since Excel 2010 we have been able to customize the ribbon. You can add your own custom tabs and then drop on to it a selection of the commands that you use the most frequently, which could even include macros.
13) Creating Charts
Your boss doesn't want to see a table full of data for the past year's sales, they want to see trends, the number of products sold each month, or the average customer evaluation results in graphical form.
Graphs and charts can be quite complex if you want them to be, but a basic chart can be produced in literally a couple of clicks, and the latest versions of Excel make it very easy to try out different charts and formats as well.
With a properly made chart, a load of data can talk to you
14) Using Array Formulas
If you need to do calculations on multiple ranges and don't want to go to the trouble of adding lots of redundant columns, array formulas are the answer. They can be quite complex and impenetrable, but they can also save you lots of time and, as a bonus, impress your colleagues.
15) Using Custom Views
How often have you carefully set up a spreadsheet for printing, got the page breaks just right, scaled it correctly, added headers and footers, and then had to change it all again to print out a different region? It can be really frustrating to set up a spreadsheet for printing time and time again, and this is where custom views can help.
A custom view will record all of your current print settings and allow you to re-apply them instantly at a later stage. As well as print settings, they can record filters and hidden rows and columns.
16) Grouping and Outlining
If you have a lot of columns or rows on your spreadsheet, it can be a bit of a chore constantly scrolling left and right or up and down to get to the point where you want to be, only to then have to go back to where you started. Grouping and outlining can help with this by allowing you to quickly expand and collapse a number of rows or columns instantly. It's like a super hide/unhide features and once you understand it, it's very easy to apply.
17) Locking Headers
How often have you found yourself on row 987 of your spreadsheet only to realize that you can't remember what the values in the columns are? This is a common problem, especially when you have to work with lots of number of columns with similar values.
The answer to this problem is to lock or freeze your header row or columns. Excel makes it very easy to ‘freeze' the top rows or first column of your spreadsheet, so as you scroll, the headers will always be visible.
Read More: How to Lock and Unlock Certain/Specific Cells in Excel
18) Automating Complex Tasks with Macros
Macros are an incredibly useful and powerful tool in Excel. With macros, you can make Excel do things that it can't do already, or take those tasks that take you an hour to complete and do them in a couple of seconds.
Although macros can be very complex and the programming side can take a bit of learning, it is possible to create useful and time-saving macros without knowing anything about programming. If you want to give it a try, there's a more detailed guide on the How-To Geek blog. Or you can use ExcelDemy.com's complete step by step guide on Excel VBA.
19) Automating Sub-totals
One of the most common tasks in Excel is to add subtotals to a column of values, for example, if you have a sheet full of sales data and you want to show how much of each product was sold. In this case, you could insert new rows after a group of products and then sum the values above and then repeat the process for each product.
I have come across people who spend hours each month doing just that, which is a huge time-waster. The sub-totals tool will do the same job in seconds and, when you're finished, it can also remove the totals just as quickly, leaving your spreadsheet exactly as it was.
Using the Subtotal function is a huge help and saves time
20) Filtering
When you are dealing with large sets of data, you often only need to look at a particular subset of that data. Rather than searching for the data by scrolling up and down, the smart solution is to filter your database.
Filtering using auto-filter is quick and easy and will allow you to get the data you are interested in inefficiently. Recent versions of Excel also have lots of pre-set filters to quickly find text, numbers, and date ranges.
And there you have it. 20 great skills for you to learn that will improve the way you use Excel and make you more productive.
Are there any other Excel features you would have put on the list? Let us know in the comments below.
[This is a guest post by Jordan James of https://www.activia.co.uk/]
Features Within Microsoft Excel
Welcome to my Excel blog! It took me some time to be a fan of Excel. But now I am a die-hard fan of MS Excel. I learn new ways of doing things with Excel and share here. Not only how to guide on Excel, but you will get also topics on Finance, Statistics, Data Analysis, and BI. Stay tuned!

